Breast cancer
of interest
are looking at
saved
next event
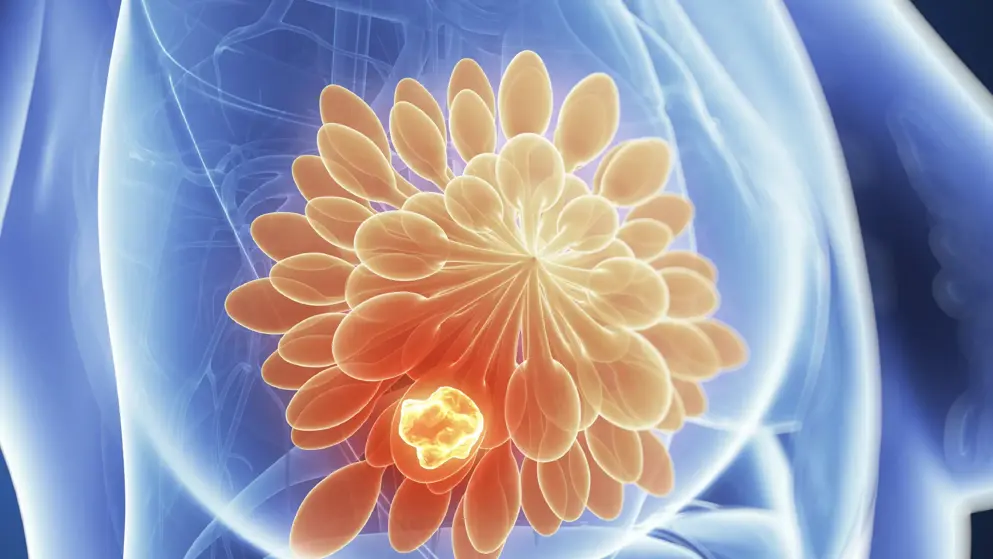
Breast cancer ranks as the most commonly diagnosed cancer worldwide, accounting for 12.5% of all new cancer cases in 2020. While it predominantly affects women over the age of 50 – who represent 80% of diagnoses – it can also occur in younger women, where it often presents more aggressively.
The most prevalent form, invasive ductal carcinoma (IDC), begins in the milk ducts and spreads into surrounding breast tissue. Lobular carcinoma, the second most common type, arises in the milk-producing lobules, and also spreads locally. By contrast, ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) is a non-invasive form confined to the ducts, without extension into surrounding tissue.
How does breast cancer typically present?
Patients often notice a palpable breast lump, nipple inversion, skin changes (e.g., dimpling, erythema), or nipple discharge.
How is breast cancer diagnosed?
Clinicians typically perform a clinical examination, followed by imaging (mammography, ultrasound, or MRI), and a core needle biopsy to confirm the diagnosis.
How are staging and treatment determined?
Staging depends on tumor size, nodal status, and distant metastases, assessed through selective imaging (e.g., CT, PET, bone scan).
Treatment plans reflect the tumor biology and stage, and often combine surgery (lumpectomy or mastectomy), radiotherapy, and systemic therapies, such as chemotherapy, endocrine therapy, HER2-targeted agents, or immunotherapy.
Identifying hormone or protein receptors on tumor cells helps guide treatment by indicating whether the cancer is driven by estrogen, progesterone, or other targets (e.g., HER2).
What factors influence risk and prevention?
Risk of breast cancer increases with age, but can also affect younger women and, though rarely, men. Other risk factors include female sex, BRCA gene mutations, dense breast tissue, prior chest radiation, hormone therapy use, alcohol consumption, and obesity.
Prevention strategies focus on lifestyle modification, risk-reducing medications, and prophylactic surgery.
Developed by EPG Health for Medthority, independently of any sponsor.
ASCO 2024 A high-level overview
From ASCO 2024, read Dr Ben Gallarda’s overview of ASCO’s commitment to palliative care, artificial intelligence, and coordination with organizations.
Abemaciclib: a newcomer in the treatment of HR+/HER2− early breast cancer
Abemaciclib, a CDK4/6 inhibitor, is the first adjuvant in 16 years to be added to endocrine therapy for HR+/HER2− early breast cancer and the first of its class to receive FDA and EMA approval for this indication.
Browse older resources
Breast Cancer 2023 Wrapped
End of 2023 review of major advancements in HER2+ breast cancer with content from recently held SABCS and other major oncology congresses
ESMO Breast Cancer 2022 – Congress Highlights
Follow all the latest developments with daily highlights from the European Society of Medical Oncology Breast Cancer Congress in Berlin, Germany, 3–5 May 2022.
Future breast cancer care: ESMO Breast Cancer 2024
Congress coverage of ESMO Breast Cancer 2024, featuring the latest advances in research, treatment updates, expert interviews, and key takeaways.
Symposium Overview
The 44th Annual San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium (SABCS) 2021 was its first hybrid meeting.
St. Gallen International Breast Cancer Conference 2023 - Day 1
Highlights and key developments from the 2023 St. Gallen International Breast Cancer Conference, 15-18 March in Vienna